Identify use cases with the value vs feasibility matrix
A step-by-step guide to identifying valuable AI use cases
The advent of Generative AI, like ChatGPT, has completely changed the playing field. You no longer need to create models from scratch; you can simply integrate an existing one. This opens doors to unprecedented possibilities and enhancements.
Ok, so you’re interested in AI. How to get started?
The success of integrating AI heavily depends on choosing the right AI use case. The AI projects that fail are often those that should never have been initiated.
Like with a lot of things in business: you start with the problem, not with the solution.
This blog provides a practical guide for businesses to identify the right AI projects to start on.
I will cover:
- What is an AI use case?
- What makes a good AI use case?
- The AI ideation method: Scope, Ideate, Evaluate
- Conclusion
Please note that this article is focused on Generative AI. I use the term AI for Generative AI for simplicity.
I use practical examples of a fictional brewery BeerCompany and write them in italics.
What is an AI use case?
AI is a general purpose technology, just like electricity. Electricity can be used for uncountable cases: toast bread, trade stocks, drive a car, well you name it. With AI, the options are truly limitless and growing at an unprecedented speed. To have a peace of mind in this chaos of possible use cases I find it useful to categorize these use cases since they have different characteristics.
3 use case categories:
Employee augmentation
At the employee level, ready to use.
Characteristics: lowest risk, but also least amount of efficiency gain. Implementing is more about education and change management.
Example: A BeerCompany sales employee uses ChatGPT for market analysis to quickly scan over all retailers in a region.
Automating business processes
At the business process level, requires building some software.
Characteristics: greater possible efficiency gain, but also has more risk.
Example: a tool that allows business analysts to easily search through all historic brewery process documentation.
Inventing new products or services
At the strategic and customer level, requires building some software.
Characteristics: not about efficiency, but about more revenue, new revenue streams or new business models.
Example: BeerCompany creates an online tool with AI-enhanced personalized beer chooser.
What makes a good AI use case?
Great, now we know what we mean with an AI use case. Before we delve into where to look for them, it's crucial to understand the basis on how they are evaluated.
A use case essentially has two core metrics: Value and Feasibility.
While value is important, you always want your idea to have high feasibility. There are three reasons for this:
- A success at the start of your AI journey is necessary for further management support.
- They involve less risk, and get done faster and cheaper.
- You are still learning how to implement and integrate AI projects.
Assessing value and feasibility is not an exact science, especially not in the ideation phase. But it’s crucial that you can come to a approximation as a team, at least as a ranking. Business professionals are typically quite adept at assessing the value of a use case. Feasibility, being mostly a technical aspect, requires a specialist for an accurate evaluation.
There are the subcriteria of each that can help you assessing the two core metrics. Later on, if you dive deeper in the most potential use case to refine it to a business case, you can use this list for a more thorough assessment.
Subcriteria value:
- High potential for cost reduction or profit increase
- Clear value proposition
- Strategic alignment
- Measurable results
Subcriteria feasibility:
- Available technology capabilities
- Data availability and quality
- Compatibility with existing systems
- Privacy and security
- Available expertise
- Cost
Now that you know what encompasses a good AI use case, let’s move to the exciting part: brainstorming!

A look inside the brewery of fictional BeerCompany
AI ideation method
Again, in blue, we will provide an ongoing example of a fictitious brewery, BeerCompany.
This method involves three steps:
- Scope your brainstorm
- Brainstorm
- Evaluate with the value vs feasibility matrix
1. Scope your brainstorm
It's important to have a clear picture of where your company creates the most value and where their pain points lie. To name an example, automatically generating monthly financial reports can be very useful but might not be a priority.
Note that this scoping works best for the Automating business processes category. For ideating truly disruptive AI applications, you probably want to look outside your value chain.
Identify the primary activities:
These are the steps that directly contribute to creating your product or service.
For BeerCompany, the primary activities include ingredient selection, the brewing process, packaging, marketing and distribution, and customer service.
Identify supporting activities:
These are the steps essential for the effective functioning of your primary activities.
This includes the development of new beer recipes, quality control, supplier management, and IT infrastructure management.
Analyze where most value Is added:
This could be a department that works exceptionally efficiently or a step in the process where your customers attach great value.
At BeerCompany, significant value is added in the beer quality (brewing process), marketing, and supplier relationships.
Identify pain points and opportunities:
Look for areas above where processes are inefficient or where customer satisfaction can be improved. These are key indicators of where an AI solution can add value.
For example, within marketing, inefficiencies may occur in the design process, responding to customer feedback, and keeping up with market trends.
This analysis provides a solid foundation for your brainstorming session, offering a clear overview of where your company stands and potential opportunities for AI integration. With this information in hand, you are better prepared to focus on brainstorming AI use cases that can truly make a difference for your business.

The latest beer of BeerCompany
2. Brainstorm by core function
Focus on specific questions in the brainstorm
Concentrate on specific questions relevant to each core function. Pay attention to pain points and how you can address them.
For marketing, BeerCompany asks these questions while brainstorming:
- How can we better understand and respond to customer behavior?
- In what ways can we personalize and optimize our marketing campaigns?
- Is there a possibility to analyze real-time market trends and respond quickly?
Brainstorm 🧠 🌪
Give everyone individual a couple of minutes and just go. Free format. Write it on post-its.
Brainstorm use cases for BeerCompany:
- Automatically analyze customer feedback and market trends to adapt beer recipes
- An AI-driven chatbot for retailers
- Optimizing social media ad placements
- Set up a competitor analysis
- Creating personalized marketing campaigns
- Real-time adjustment of pricing strategies
Evaluation: value vs feasibility matrix
Great. Now we have a list of potential business cases! Now discuss your ideas with the group and come to a consensus on where to plot them on the value vs feasibility matrix.
The value vs feasibility matrix is a tool to prioritize your ideas. All ideas will land in one of 4 quadrants:
- Sweet spot: high value - high feasibility
- Easy win: low value - high feasibility
- Long-term goals: high value - low feasibility
- Low priority: low value - low feasibility
Realize that you don’t have the full information. So don’t be too precise. For example, you probably don’t know yet how valuable an AI-driven competitor analysis will be. Or optimizing ad placements with AI is very hard to build yourself, but probably there is a tool available but you don’t know if that suits your needs. The goal here to come up with one or two sweet spot ideas. An additional goal is to train you to think about the benefits and risks of AI solutions.
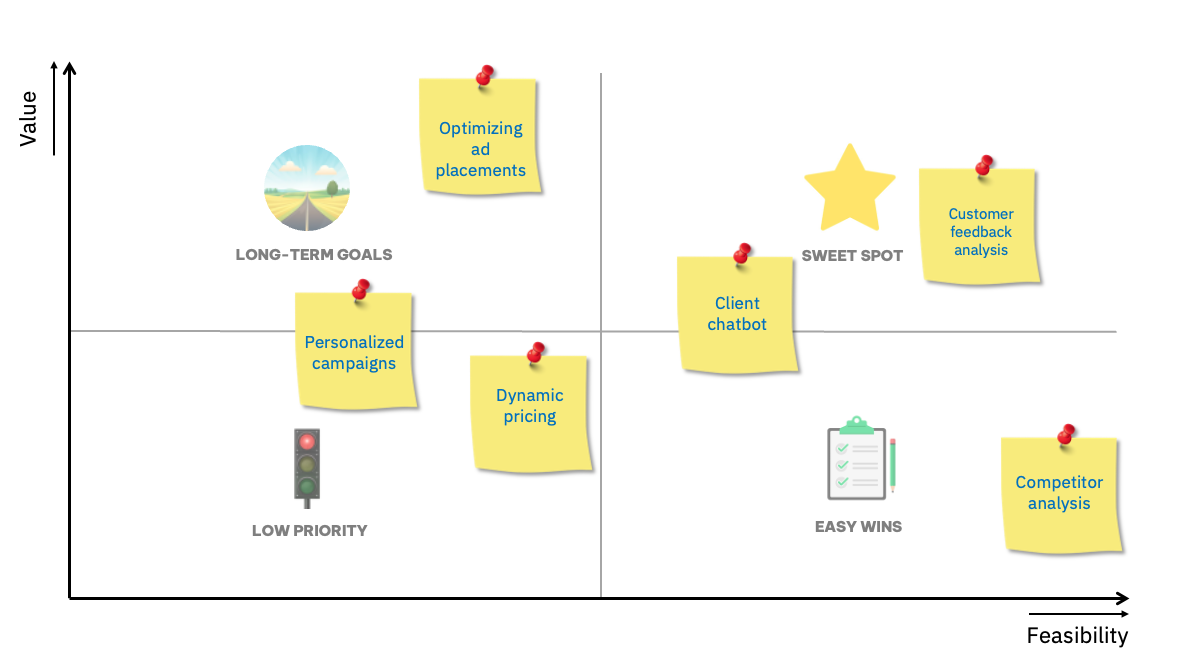
Value vs feasibility matrix with examples
We've identified several promising AI initiatives for BeerCompany! At this stage, the analysis of customer feedback emerges as the top choice. However, the competitor analysis might be a more suitable initial project, considering its high feasibility. Additionally, the client chatbot stands out as another compelling idea.
For BeerCompany, the advisable next steps are:
- Dive deeper and develop detailed business cases for these three ideas
- Sprint towards your first measurable AI application
Beyond these immediate steps, BeerCompany’s broader AI integration strategy should include:
- Establish an AI committee to gather insights from the ground up
- Create company-wide AI guidelines
- Invest in training and education
- Expanding to other AI applications
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of AI in business, it's clear that the key to successful AI integration lies in smartly identifying and evaluating use cases. For companies like BeerCompany, and indeed any business eager to dive into AI, it's about more than just adopting new technology. It’s about strategically embedding AI into their core operations.
This involves not just recognizing where AI can add significant value, but also understanding the practical aspects of its implementation. By effectively assessing both the value and feasibility of AI applications, businesses are well-positioned to leverage AI’s transformative potential.
Thank you for reading!
Sophron Vermeij
At Waive, we understand the unique challenges every organization faces when integrating AI. We help companies jointly discover AI and successfully integrate it into their business processes. Only with AI will you be well-prepared for the future. And it's not just about technology; it's about transforming processes and seizing new opportunities as well
The future won't wait, and the development of AI doesn't stand still. Start exploring the possibilities today. Contact me for a free exploratory conversation and discover how Waive can guide you in taking this important step into the future.

